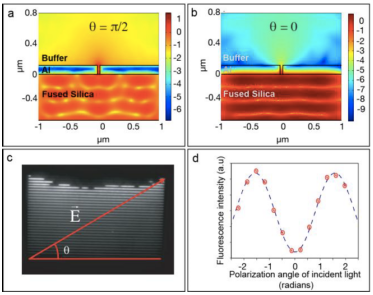
Abstract
Resolving single fluorescent molecules in the presence of high fluorophore concentrations remains a challenge in single-molecule biophysics that limits our understanding of weak molecular interactions. Total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) imaging, the workhorse of single-molecule fluorescence microscopy, enables experiments at concentrations up to about 100 nM, but many biological interactions have considerably weaker affinities, and thus require at least one species to be at micromolar or higher concentration. Current alternatives to TIRF often require three-dimensional confinement, and thus can be problematic for extended substrates, such as cytoskeletal filaments. To address this challenge, we have demonstrated and applied two new single-molecule fluorescence microscopy techniques, linear zero-mode waveguides (ZMWs) and convex lens induced confinement (CLIC), for imaging the processive motion of molecular motors myosin V and VI along actin filaments. Both technologies will allow imaging in the presence of higher fluorophore concentrations than TIRF microscopy. They will enable new biophysical measurements of a wide range of processive molecular motors that move along filamentous tracks, such as other myosins, dynein, and kinesin. A particularly salient application of these technologies will be to examine chemomechanical coupling by directly imaging fluorescent nucleotide molecules interacting with processive motors as they traverse their actin or microtubule tracks.